
Linux
GNU宣言
“我认为:如果我喜欢一个程序的话,那我就应该将它分享给其他喜欢这个程序的人
这句话是我的座右铭。软件商想各个击破用户,使他们同意不把软件和他人分享。我拒绝以
这种方式破坏用户之间的团结。我的良心使我不会签下一个不开放的合约或是软件许可证协
议,在麻省理工学院人工智能实验室工作的多年时间里,我一直反对这样的趋势与冷漠,但
是最后事情槽糕到:我无法在一个处理事情的方法与我的意愿相违背的机构呆下去,”
“为了能继续使用电脑而不感到羞愧,我决定将一大堆自由软件集合在一起,从而使
我可以不必再使用不自由的软件。因此,我辞去了人工智能实验室的工作,不给麻省理工
学院任何法律上的借口来阻止我把GNU送给其他人…”
“很多程序员对系统软件的商业化感到不悦。这虽然可以使他们赚更多的线,但是这
使他们觉得自己与其他程序员处于对立状态,而不是同志之间的感觉。程序员对友谊的最
基本表现就是共享程序,而当前的市场运作基本上禁止程序员将其他程序员作为朋友看待,
软件购买者必须在友谊和守法之间做一选择。自然地,有很多人选择了友谊。但是那些相
信法律的人常常没办法安心地做这一选择。他们会变得愤世嫉俗,认为写程序只不过是赚
钱的一种方法而已。”
“复制全部或者部分程序对程序员来说就和呼吸一样是自然有益的事。复制软件就应
该这么自由…”
“从长远来看,免贵提供软件是迈向大同世界的一步,在那个时代中,没有人再为了生
计而努力工作。在每周10小时的必要劳动(如立法、家政服务、机器人修理和行星观察)之后,
人们自由地参与各种自己感兴趣的活动,例如编程。那时候就不必靠写程序来过活了…”
《Linux命令与shell脚本变成大全》第四版
《Unix&Linux大学教程》
什么是Linux
Unix是一种多用户、多任务处理的操作系统;
Linux是任何使用Linux内核的Unix的操作系统
文件管理系统
日志文件系统
- ex4,最大支持16T,默认有序模式,支持加密压缩及单目录不限数量的子目录
- XFS,回写模式的日志方法,高性能但是存在风险,因为实际数据并未存入日志文件
文件系统的使用
创建分区
- fdisk,只能处理2T以下的硬盘
- gdisk,如果存储设备要使用GUID分区表,就需要用到gdisk
- GNU parted,允许调整现有分区大小,可以收缩或者扩大磁盘分区
创建文件系统(格式化)
mkfs.ext4
# 创建挂载点 mkdir /home/data # 挂载磁盘 mount -t ext4 /dev/sda /home/data lsblk -f /dev /sda # 自动挂载 etc/fstabmkfs.xfs
mkfs.btrfs
卷文件系统
从一个或多个磁盘创建存储池提供了生成虚拟磁盘(卷)的能力,通过存储池可以根据需要增加卷,提供灵活性的同时大大减少停机时间
- ZFS文件系统
- Btrfs
- Stratis
LVM
LVM布局
物理卷(PV),指定一个未使用的磁盘分区或整个驱动由LVM使用
卷组(VG)(VG),用于将PV加入存储池,用于构建各种逻辑卷(LV)
逻辑卷(LV),核心步骤,由VG的存储空间块组成,可以使用文件系统格式化LV,且不能跨VG创建。当数据量超过已有文件系统上限时,只能在同一个物理磁盘内调整分区大小,逻辑卷(LV)就是用来将另外一块硬盘上的分区加入已有的文件系统来动态添加存储空间的工具
Linux中的LVM
Linux中通过lvm2软件管理LVM
首次设置逻辑卷(LV)步骤
- 创建物理卷(PV)
- 创建卷组(VG)
- 创建逻辑卷(LV)
- 格式化逻辑卷(LV)
- 挂载逻辑卷(LV)
- VG、LV扩缩容
示例
命令行清单
# 命令行帮助 [root@localhost ~]# lvm help <command> # 查看硬盘情况 [root@localhost ~]# lsblk # 1. 创建物理卷(PV) [root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/vdb /dev/vdc # 2. 创建卷(VG)组包含vdb、vdc [root@localhost ~]# vgcreate vg00 /dev/vdb /dev/vdc # 3.创建逻辑卷(LV) [root@localhost ~]# lvcreate -L 1g -v vg00 # 4.1 格式化逻辑卷(LV) [root@localhost ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg00/lvol0 # 4.2 挂载LV [root@localhost ~]# mkdir my_LV [root@localhost ~]# mount -t ext4 /dev/vg00/lvol0 my_LV # 容量变更 # 查看vg详细信息,VG中LV、PV信息 [root@localhost ~]# vgdisplay -v <vg00> # VG缩扩PV [root@localhost ~]# vgreduce vg00 /dev/vdc [root@localhost ~]# vgextend vg00 /dev/vdc # LV缩扩容量,只能使用所归属的VG容量 [root@localhost ~]# lvextend -L 10G /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 [root@localhost ~]# lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 # 刷新磁盘空间ext4 和xfs格式 [root@localhost ~]# resize2fs /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 [root@localhost ~]# xfs_growfs /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0命令行及返回
# 查看硬盘情况 [root@localhost ~]# lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT fd0 2:0 1 4K 0 disk sr0 11:0 1 490.2M 0 rom /media vda 252:0 0 40G 0 disk ├─vda1 252:1 0 1G 0 part /boot └─vda2 252:2 0 39G 0 part ├─centos-root 253:0 0 35.1G 0 lvm / └─centos-swap 253:1 0 3.9G 0 lvm [SWAP] vdb 252:16 0 100G 0 disk vdc 252:32 0 1G 0 disk # 1. 创建物理卷(PV) [root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/vdb /dev/vdc Physical volume "/dev/vdb" successfully created. Physical volume "/dev/vdc" successfully created. # 2. 创建卷组(VG)包含vdb、vdc [root@localhost ~]# vgcreate vg00 /dev/vdb /dev/vdc Volume group "vg00" successfully created [root@localhost ~]# vgdisplay --- Volume group --- VG Name centos ... --- Volume group --- VG Name vg00 System ID Format lvm2 Metadata Areas 2 Metadata Sequence No 1 VG Access read/write VG Status resizable MAX LV 0 Cur LV 0 Open LV 0 Max PV 0 Cur PV 2 Act PV 2 VG Size 100.99 GiB PE Size 4.00 MiB Total PE 25854 Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0 Free PE / Size 25854 / 100.99 GiB VG UUID 4sQhAV-ES7y-rQBe-PJLo-7PuO-479o-Y6T9sn # 3.创建逻辑卷(LV) [root@localhost ~]# lvcreate -L 1g -v vg00 Archiving volume group "vg00" metadata (seqno 1). Creating logical volume lvol0 Creating volume group backup "/etc/lvm/backup/vg00" (seqno 2). Activating logical volume vg00/lvol0. activation/volume_list configuration setting not defined: Checking only host tags for vg00/lvol0. Creating vg00-lvol0 Loading table for vg00-lvol0 (253:2). Resuming vg00-lvol0 (253:2). Wiping known signatures on logical volume "vg00/lvol0" Initializing 4.00 KiB of logical volume "vg00/lvol0" with value 0. Logical volume "lvol0" created. [root@localhost ~]# lvdisplay /dev/vg00/lvol0 --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/vg00/lvol0 LV Name lvol0 VG Name vg00 LV UUID bT0lhQ-vHVn-TXPc-9TxH-C7eU-AI8d-8FXJfw LV Write Access read/write LV Creation host, time localhost.localdomain, 2024-05-11 10:02:51 +0800 LV Status available # open 0 LV Size 1.00 GiB Current LE 256 Segments 1 Allocation inherit Read ahead sectors auto - currently set to 8192 Block device 253:2 # 4.1 格式化逻辑卷(LV) [root@localhost ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg00/lvol0 mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013) Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=4096 (log=2) Fragment size=4096 (log=2) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 65536 inodes, 262144 blocks 13107 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=268435456 8 block groups 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group 8192 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (8192 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done # 4.2 挂载LV [root@localhost ~]# mkdir my_LV [root@localhost ~]# mount -t ext4 /dev/vg00/lvol0 my_LV [root@localhost ~]# ls my_LV/ lost+found # 4.3 扩容、收缩VG&LV # 查看VG下的pv内容 [root@localhost ~]# vgdisplay -v <vg00> --- Volume group --- VG Name vg00 System ID Format lvm2 Metadata Areas 2 Metadata Sequence No 6 VG Access read/write VG Status resizable MAX LV 0 Cur LV 1 Open LV 1 Max PV 0 Cur PV 2 Act PV 2 VG Size 100.99 GiB PE Size 4.00 MiB Total PE 25854 Alloc PE / Size 1280 / 5.00 GiB Free PE / Size 24574 / 95.99 GiB VG UUID 4sQhAV-ES7y-rQBe-PJLo-7PuO-479o-Y6T9sn --- Logical volume --- LV Path /dev/vg00/lvol0 LV Name lvol0 VG Name vg00 LV UUID bT0lhQ-vHVn-TXPc-9TxH-C7eU-AI8d-8FXJfw LV Write Access read/write LV Creation host, time localhost.localdomain, 2024-05-11 10:02:51 +0800 LV Status available # open 1 LV Size 5.00 GiB Current LE 1280 Segments 1 Allocation inherit Read ahead sectors auto - currently set to 8192 Block device 253:2 --- Physical volumes --- PV Name /dev/vdb PV UUID pC2xLf-UvnW-I4zy-3pq6-d93H-7Ff8-bc2O9o PV Status allocatable Total PE / Free PE 25599 / 24319 PV Name /dev/vdc PV UUID UrrpAy-wgq3-cBF0-oWND-tdwp-E3FV-cfgA1d PV Status allocatable Total PE / Free PE 255 / 255 # VG缩扩PV [root@localhost ~]# vgreduce vg00 /dev/vdc Removed "/dev/vdc" from volume group "vg00" [root@localhost ~]# vgextend vg00 /dev/vdc Volume group "vg00" successfully extended # LV缩扩容量,只能使用所归属的VG容量 [root@localhost ~]# lvextend -L 10G /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 Size of logical volume vg00/lvol0 changed from 1.00 GiB (256 extents) to 10.00 GiB (2560 extents). Logical volume vg00/lvol0 successfully resized. [root@localhost ~]# lvextend -l 100%FREE /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 [root@localhost ~]# lvreduce -L 5G /dev/mapper/vg00-lvol0 WARNING: Reducing active and open logical volume to 5.00 GiB. THIS MAY DESTROY YOUR DATA (filesystem etc.) Do you really want to reduce vg00/lvol0? [y/n]: y Size of logical volume vg00/lvol0 changed from 10.00 GiB (2560 extents) to 5.00 GiB (1280 extents). Logical volume vg00/lvol0 successfully resized.
实战
本地yum源
系统环境
[root@localhost repo]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)防火墙&SELinux
# 开启防火墙80端口 [root@yumserver ~]# firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent success [root@yumserver ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success # 临时关闭、开启SElinux setenforce 0 setenforce 1 # 永久关闭SELinnux [root@yumserver ~]# cat /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=disabled # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected. # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted添加阿里云yum源
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ [root@localhost yum.repos.d]# ls bak bakcup CentOS-Base.repo epel.repo # 获取阿里云yum配置文件 curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo https://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/epel.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo yum makecache yum repolist安装同步软件
yum-utils:reposync同步工具
createrepo:编辑yum库工具
httpd:通过Apache软件提供web服务
yum install -y wget make cmake gcc gcc-c++ pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel httpd yum-utils createrepo同步阿里云yum源到本地指定目录/mirror
mkdir -p /mirror chown -R apache:apache /mirror chmod -R 755 /mirror ###参数-n指下载最新软件包,-p指定目录,指定本地的源--repoid(如果不指定就同步本地服务器所有的源),下载过程比较久 reposync -n --repoid=extras --repoid=updates --repoid=base --repoid=epel -p /mirror [root@yumserver ~]# du -sh /mirror/* 9.0G /mirror/base 16G /mirror/epel 321M /mirror/extras 2.2G /mirror/updates创建仓库索引
createrepo -po /mirror/base/ /mirror/base/ createrepo -po /mirror/extras/ /mirror/extras/ createrepo -po /mirror/updates/ /mirror/updates/ createrepo -po /mirror/epel/ /mirror/epel/- 更新数据源
createrepo --update /mirror/base/ createrepo --update /mirror/extras/ createrepo --update /mirror/updates/ createrepo --update /mirror/epel/- 启动httpd及增加对应配置
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd systemctl status httpd [root@yumserver ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf ### 增加以下配置 ... DocumentRoot "/mirror/" <Directory "/mirror/"> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride None Order allow,deny Allow from all Require all granted </Directory> ...- 更新index.html
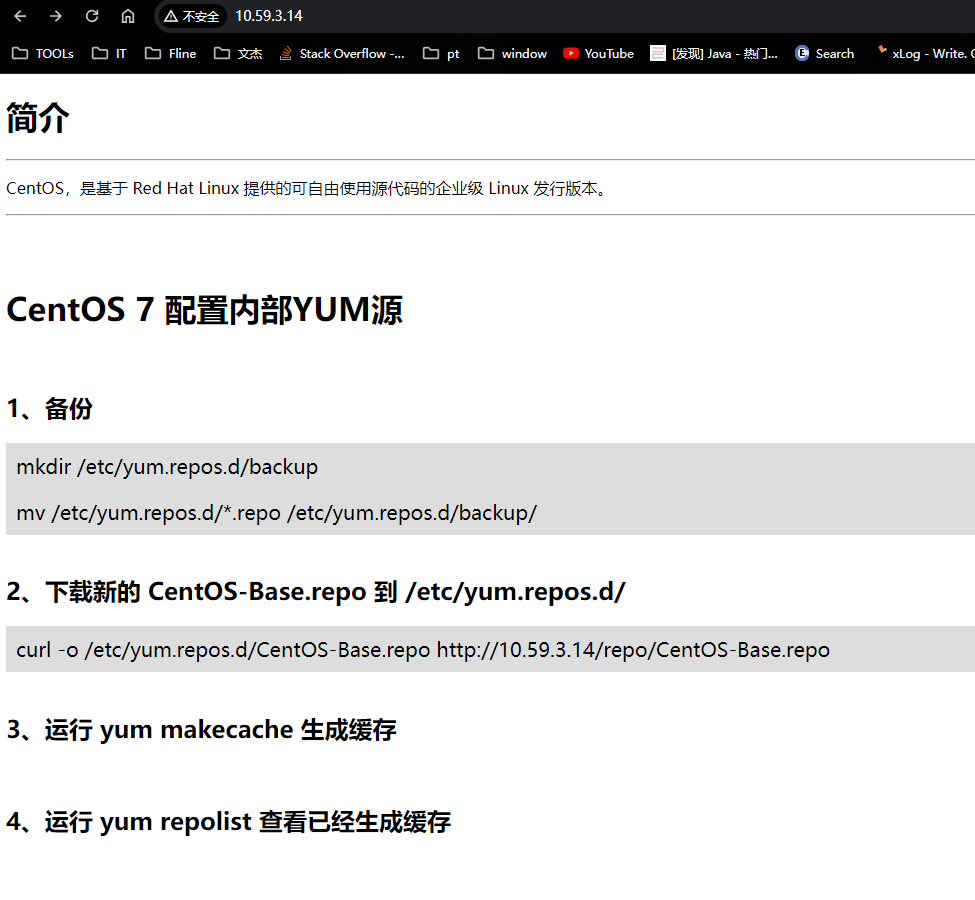
cat << EOF > /usr/share/httpd/noindex/index.html <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>CentOS 7 镜像</title> <script>document.createElement("myHero")</script> <style> myHero { display: block; background-color: #ddd; padding: 10px; font-size: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1>简介</h1> <hr> <p>CentOS,是基于 Red Hat Linux 提供的可自由使用源代码的企业级 Linux 发行版本。</p> <hr> <br> <br> <h1>CentOS 7 配置内部YUM源</h1> <br> <h2>1、备份</h2> <myHero>mkdir /etc/yum.repos.d/backup </myHero> <myHero>mv /etc/yum.repos.d/*.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/backup/</myHero> <br> <h2>2、下载新的 CentOS-Base.repo 到 /etc/yum.repos.d/ </h2> <myHero>curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://10.59.3.14/repo/CentOS-Base.repo</myHero> <br> <h2>3、运行 yum makecache 生成缓存</h2> <br> <h2>4、运行 yum repolist 查看已经生成缓存</h2> <br> <br> </body> </html> EOF- 创建客户端需要的源配置文件
[root@localhost repo]# pwd /mirror/repo [root@localhost repo]# vi CentOS-Base.repo ### CentOS-Base.repo [base] name=CentOS- - Base - 10.59.3.14 failovermethod=priority baseurl=http://10.59.3.14/base/ enable=1 gpgcheck=0 #released updates [updates] name=CentOS- - Updates - 10.59.3.14 failovermethod=priority baseurl=http://10.59.3.14/updates/ enable=1 gpgcheck=0 #additional packages that may be useful [extras] name=CentOS- - Extras - 10.59.3.14 failovermethod=priority baseurl=http://10.59.3.14/extras/ enable=1 gpgcheck=0 #additional packages that may be useful [epel] name=CentOS- - Epel - 10.59.3.14 failovermethod=priority baseurl=http://10.59.3.14/epel/ enable=1 gpgcheck=0- 配置自动更新脚本
#!/bin/bash # 设置日志文件名 LOG_FILE="/var/log/aliyunYumUpdatelog.log" # 执行 createrepo 命令 createrepo --update /mirror/base/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1 createrepo --update /mirror/extras/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1 createrepo --update /mirror/updates/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1 createrepo --update /mirror/epel/ >> $LOG_FILE 2>&1 # 检查命令是否成功执行 if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "$(date +%Y-%m-%d)_aliyum_yum update successful" >> $LOG_FILE else echo "$(date +%Y-%m-%d)_aliyum_yum update failed" >> $LOG_FILE fi# 定时运行脚本(周日12点) 0 12 * * 0 /mirror/script/aliyum_update.sh- 效果
防火墙
firewall-cmd
在CentOS 7中,新引入了firewalld防火墙,取代了CentOS 6之前的iptables防火墙。
iptables用于过滤数据包,属于网络层防火墙。iptables主要是基于接口,来设置规则,从而判断网络的安全性。
firewalld能够允许哪些服务可用,哪些端口可用等等,属于更高一层的防火墙。firewalld提供了支持网络区域所定义的网络链接以及接口安全等级的动态防火墙管理工具。它支持IPv4、IPv6防火墙设置以及以太网桥(在某些高级服务可能会用到,比如云计算), 并且拥有两种配置模式:运行时(Runtime)模式、永久(Permanent)模式。
firewalld和iptables都是用来管理防火墙的工具(属于用户态)来定义防火墙的各种规则功能,内部结构都指向netfilter网络过过滤子系统(属于内核态)来实现包过滤防火墙功能。
firewalld自身并不具备防火墙的功能,而是和iptables一样需要通过内核的netfilter来实现,也就是说firewalld和 iptables一样,他们的作用都是用于维护规则,而真正使用规则干活的是内核的netfilter,只不过firewalld和iptables的结构以及使用方法不一样罢了。firewall-cmd是firewalld的字符界面管理工具,firewall-config是firewalld的图形用户界面管理工具。
firewalld是centos7的一大特性,最大的好处有两个:支持动态更新,不用重启服务;第二个就是加入了防火墙的“zone”概念。
首先,将所有网络流量分为多个区域(zone),然后,根据数据包的源IP地址或传入的网络接口等条件将流量传入相应区域,同时,每个区域都定义了自己打开或者关闭的端口和服务列表。
常用操作
# 查看状态
systemctl status firewalld
firewall-cmd --state
# 开启/关闭/重启
systemctl start firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
systemctl restart firewalld
# 查看是否开机自启、开机自启
systemctl is-enabled firewalld
systemctl enable firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
# 白名单及端口开放
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/tcp
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="10.59.88.6" port protocol="tcp" port="3306" accept"
firewall-cmd --permanent --remove-rich-rule="rule family="ipv4" source address="10.42.136.247" port protocol="tcp" port="3306" accept"
# 默认开启了22端口的public权限,关闭public权限
sudo firewall-cmd --list-services
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --remove-service=ssh
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
# 防火墙清单
firewall-cmd --list-all
# 重载防火墙(不中断服务、中断服务)
firewall-cmd --reload
firewall-cmd --complete-reload
iptables
iptables 是一个基于用户空间的防火墙工具,用于配置 Linux 内核防火墙的规则集。它可以用来过滤、修改和转发网络数据包
SELinux
Security-Enhanced Linux简称SELinux,它是一个Linux内核模块,也是Linux的一个安全子系统。
SELinux的结构及配置非常复杂,而且有大量概念性的东西,学习难度较大。很多Linux系统管理员嫌麻烦都把SELinux关闭了。
系统资源都是通过进程来读取更改的,为了保证系统资源的安全,传统的Linux使用用户、文件权限的概念来限制资源的访问,通过对比进程的发起用户和文件权限以此来保证系统资源的安全,这是一种自由访问控制方式(DAC);但是随着系统资源安全性要求提高,出现了在Linux下的一种安全强化机制(SELinux),该机制为进程和文件加入了除权限之外更多的限制来增强访问条件,这种方式为强制访问控制(MAC)。这两种方式最直观的对比就是,采用传统DAC,root可以访问任何文件,而在MAC下,root只能访问设定允许的文件。
# 关闭SELinux
[root@snow ~]# vim /etc/selinux/config
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of three values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# minimum - Modification of targeted policy. Only selected processes are protected.
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
工具
yum
apt-get
rpm
简介
RPM的全名是Red Hat Package Manager,本意是Red Hat 软件包管理,顾名思义是Red Hat 贡献出来的软件包管理
优缺点
优点
由于已经编译完成并且打包,所以安装很方便
由于套件信息已经记录在Linux主机的数据库中,方便查询、升级与卸载
缺点
安装环境必须与打包时的环境一致
需要满足软件的依赖属性需求
卸载时需要特别小心,最底层的软件不可以先删除,否则可能造成整个系统出问题
dpkg
路由
路由选择顺序
在不考虑策略路由等其他情况下,对IP包进行路由时,通常按照如下顺序进行。
最长掩码匹配原则
管理距离/AD/路由协议优先级
路由花销/Cost/Metric
设置永久静态路由
双网卡定向设置路由
centos有两张网卡分别为192网段和10网段,要求分别使用各自的网关
业务场景为服务器192内网需要映射到外网215上提供服务,10网段真实地址为接口等应用使用的真实地址
实现:
# 设置eth0走10网段网卡
route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 gw 10.59.0.254
# 设置脚本自动启动
cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
touch route-eth0
vi route-eth0
···
#!/bin/bash
route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 gw 10.59.0.254
···
chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth0
sudo touch /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-local
sudo chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-local
vi ifup-local
···
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth0
···
# 查看route
route -n
···
# 设置eth0走10网段网卡
route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 gw 10.59.0.254
route add -net 10.42.248.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw 192.168.200.254
# 设置脚本自动启动
cd /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/
touch route-eth0
vi route-eth0
···
#!/bin/bash
route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 gw 10.59.0.254
···
chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth0
sudo touch /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-local
sudo chmod +x /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifup-local
vi ifup-local
···
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/route-eth0
···
# 查看route
route -n
···
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
0.0.0.0 192.168.200.254 0.0.0.0 UG 121 0 0 eth1
10.0.0.0 10.59.0.254 255.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
10.42.248.0 192.168.200.254 255.255.255.0 UG 0 0 0 eth1
10.59.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 120 0 0 eth0
192.168.200.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 121 0 0 eth1
···



